Biogenic Organotropic Wetsuits
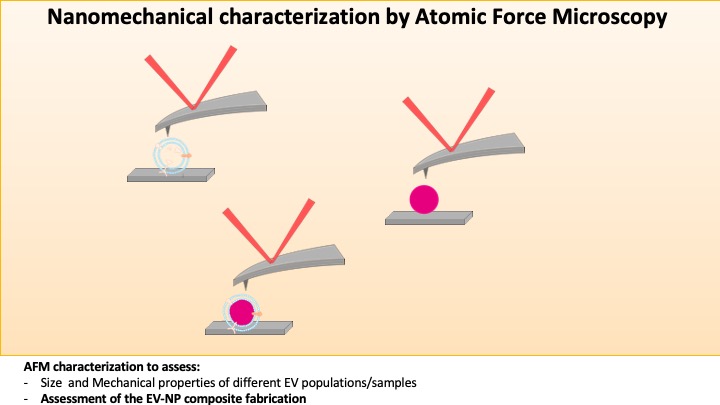
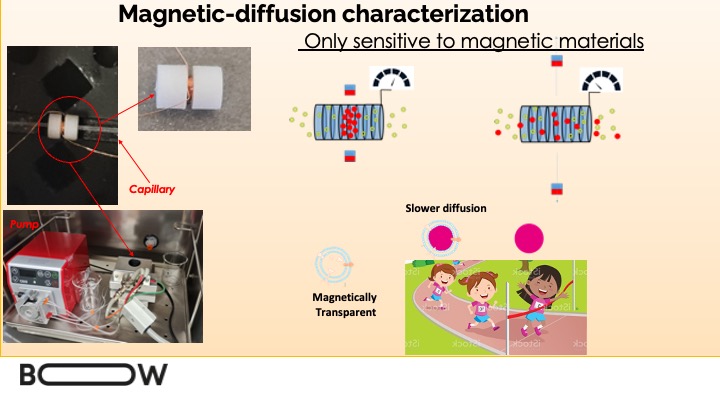
The main objective of BOW is to create hybrid magnetic nanoparticles with a membrane surface made from an extracellular vesicle. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are the universal shuttles of intercellular communication, transferring lipids, proteins and nucleic acids, mediating physiological processes and spreading various diseases, including cancer and infections. The main goal of the EU-funded BOW project is to explore and develop the technology capable of lending the biological surface precision, circulation and targeting abilities of EVs to superparamagnetic nanodevices by coating them with a single- or multi-layer EV membrane. This technology aims to advance implantable nanodevices and nanomaterials towards sustainable production and clinical translation, proving the possibility of recapitulating biomimetic functions on any synthetic nanodevice.
Partner
-
Consorzio interuniversitario per lo sviluppo dei Sistemi a Grande Interfase (IT)
-
Consiglio Nazionale Delle Ricerche (IT)
-
Universidad de Santiago de Compostela (ES)
-
Max-Planck-Institut für Polymerforschung (DE)
-
Zabala Innovation (ES)
-
Helmholtz Zentrum München Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Gesundheit und Umwelt (DE)
-
Institute of Technology Sligo (IE)
-
Eidgenoessische Technische Hochschule Zuerich (CH)
-
Hansabiomed Life Sciences Ou (EE)
-
Biodevice Systems Sro (CZ)
-
Rigenerand srl (IT)